Patients with cerebral palsy, neuromuscular disease or severe and multiple disabilities may suffer from ventilatory disorders due to respiratory muscle weakness, chest deformities, dysphagia and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Bronchial congestion, therefore, might occur.
SESOBEL’s specialized Respiratory Unit provides treatment and prevention for children and the young in need.
Respiratory management consists of:
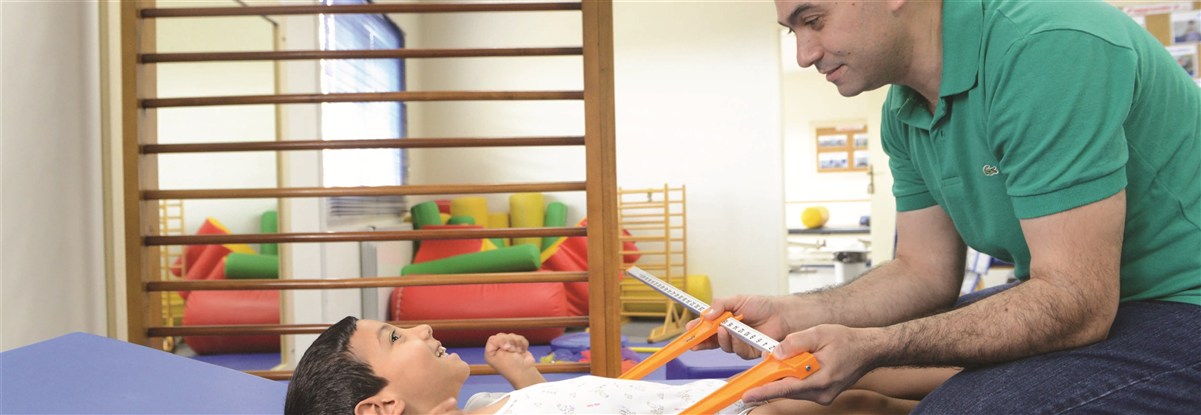
- Assessment of patients’ respiratory conditions conducted by a physiotherapist.
- Pneumological Consultations: organized by physiotherapist and run at SESOBEL in collaboration with pneumologists and pediatric pneumologists.
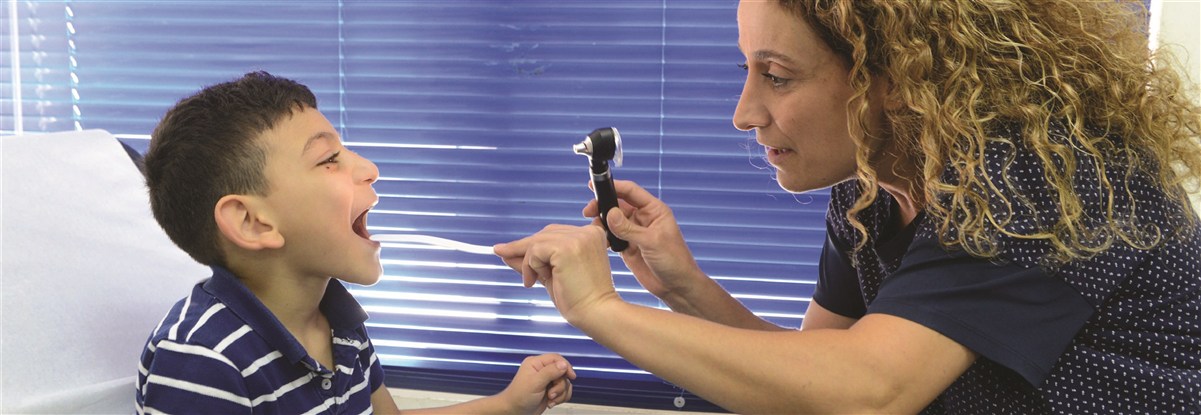
During consultations, doctors might ask for additional tests in order to devise treatment plans appropriate for children’s health conditions.
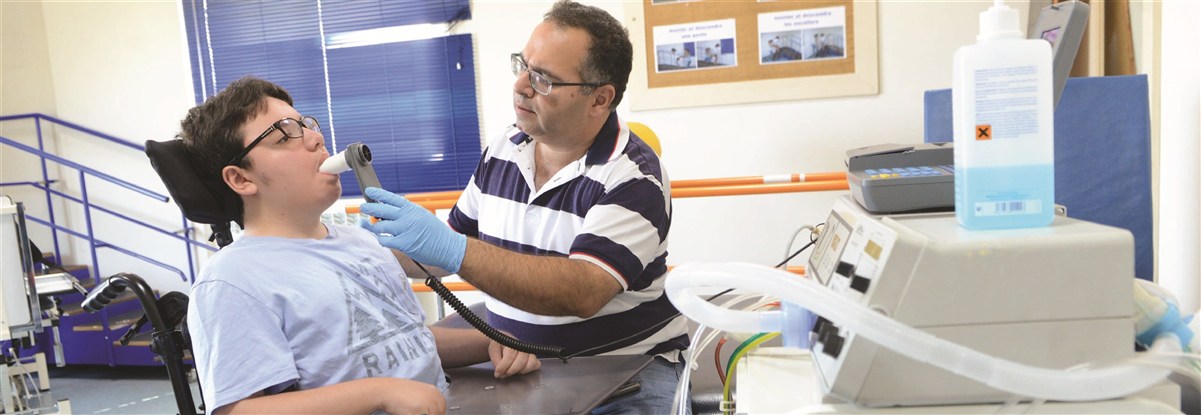
-Tests may include radiography, pulse oximetry, capnography, polygraphy, pulmonary function tests (PFT), as well as arterial blood gas test (ABG). They might be carried out at hospitals, the centre or home.
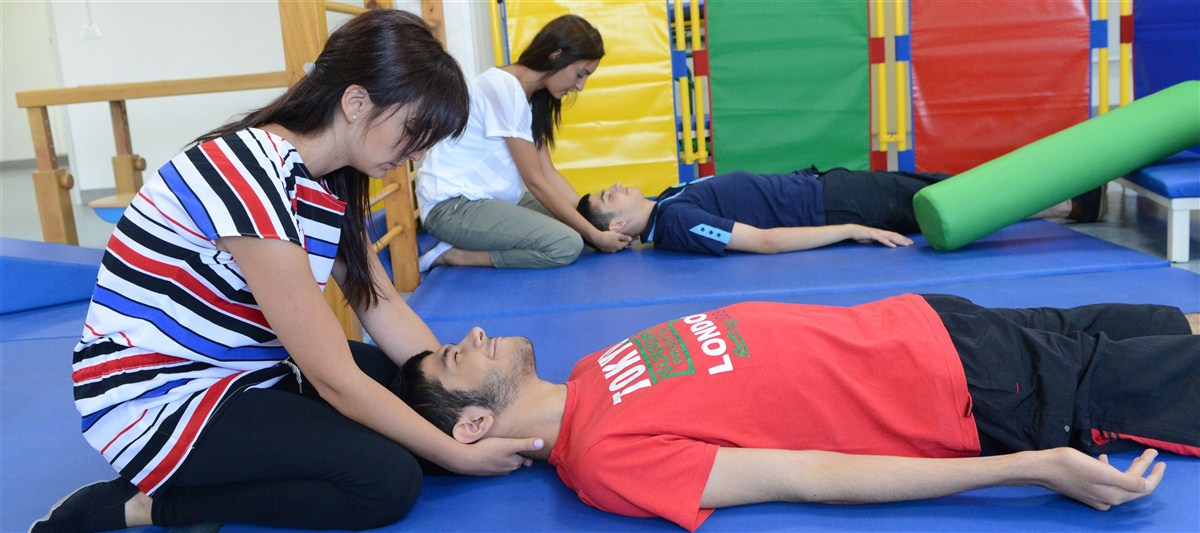
- Respiratory treatment includes manual or instrumental techniques that depend on every child’s illness, age, tolerance, fatigability during treatment, as well as congestion.
*Manual treatment consists of active and passive mobilization of the chest, airway clearance maneuver, as well as directed or induced cough.
*Instrumental treatment requires the use of devices such as IPPB (like Alpha and Porta Bird) and cough-assist devices.
Treatment could be carried out at the centre or at home.
In case of respiratory failure, noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is prescribed and performed while devices such as BiPAP and CPAP ventilators and oxygen concentrators.
-Parental guidance: Physiotherapists should provide the family with simple manual techniques for airway clearance and the use of ventilation devices in order to prevent accidents and ensure treatment continuity.
The Emergency Service is available 24/ 24 for parents and is ready to respond to different demands anytime.