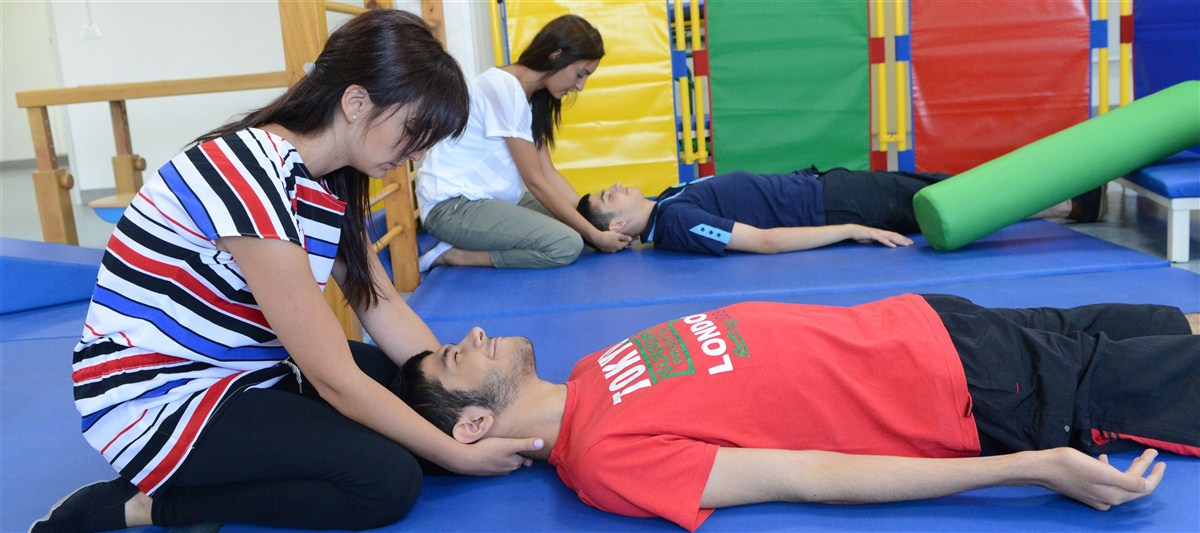
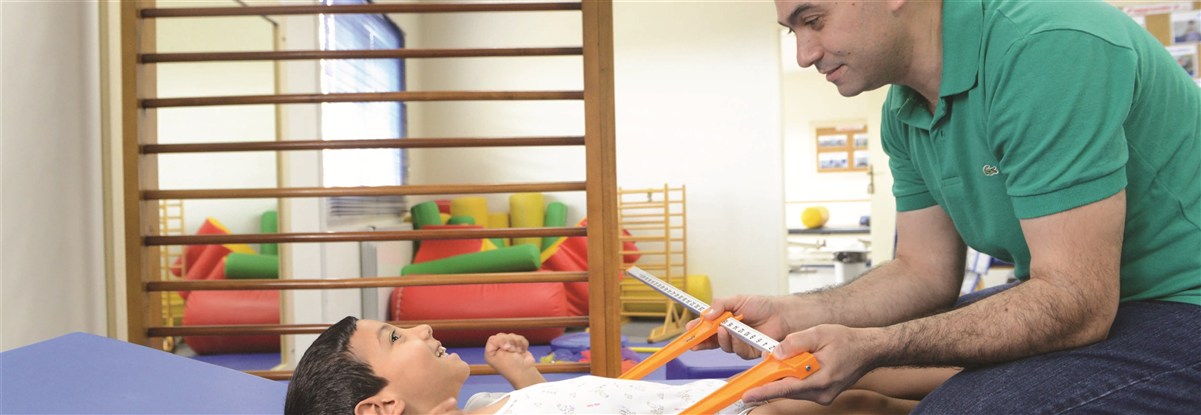
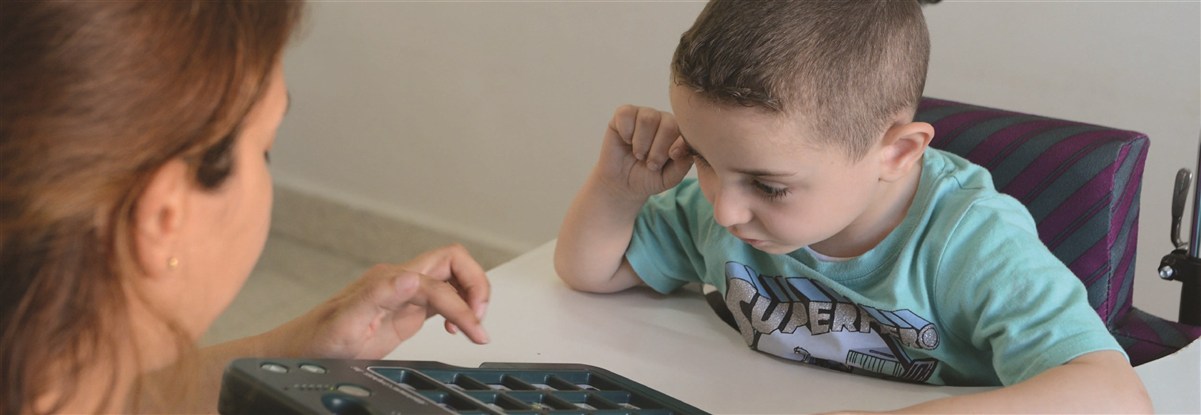
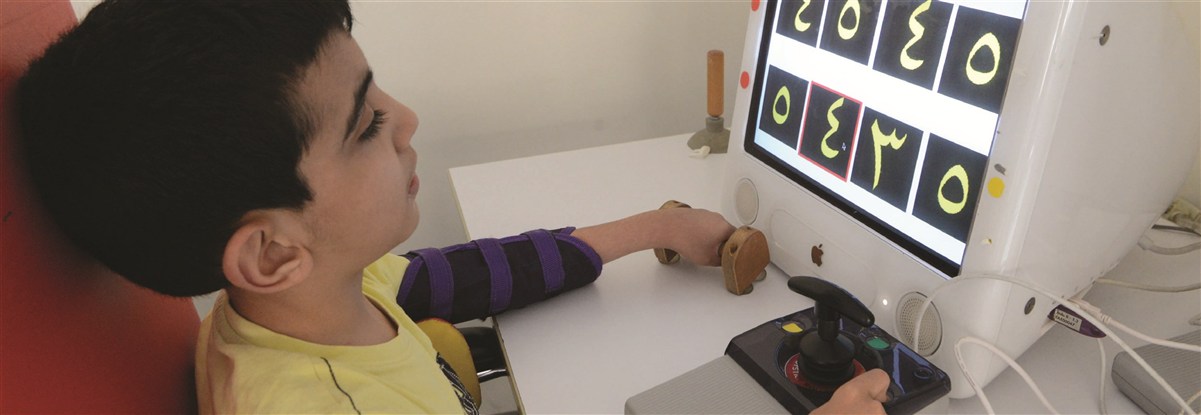
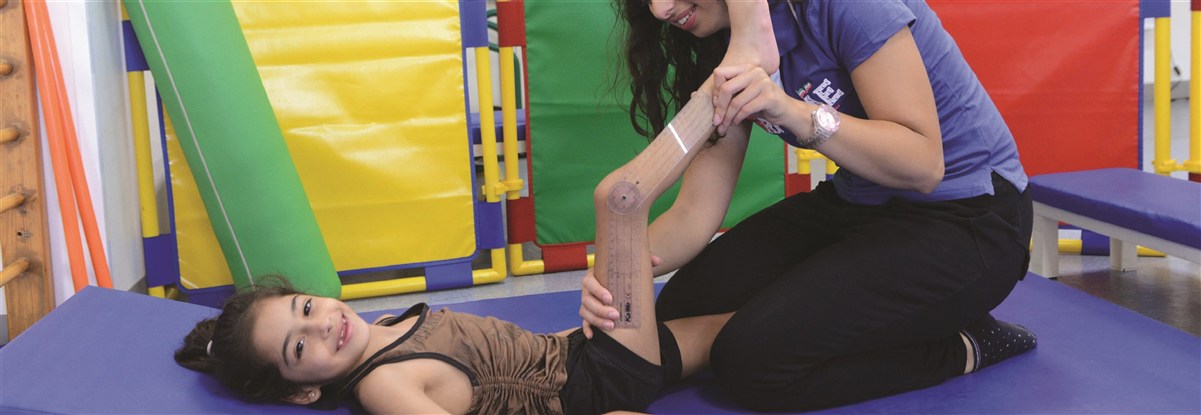
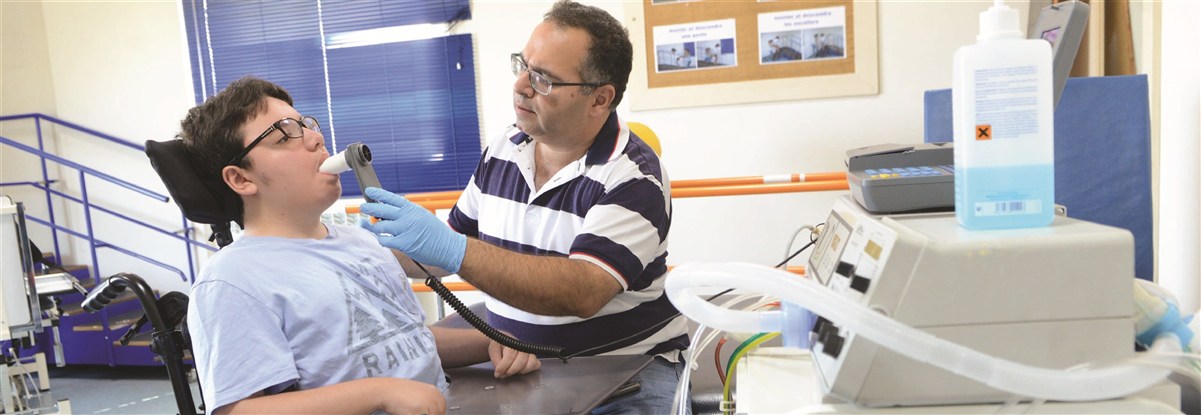
The upper limbs of children with cerebral palsy or degenerative diseases may show problems with muscle tone (spasticity, fluctuating tone or hypotonia) involuntary movements, disease patterns ... etc.) That limits the function, therefore the achievement, of quotidian occupations.
Care and support include:
-Assessment of motor skills with appropriate tests (motor, functional, prehension)
- Rehabilitation objectives:
Inhibiting spasticity and disease patterns
Creating awareness of upper limbs and their functions
Stimulating gross motor skills
Developing fine motor skills
-Manufacturing hand splints: Two types of hand splints are available for children:
Posture splint that are used to place hands in proper position to allow them to gain articular amplitude and prevent their deformation
Functional splint that facilitate handgrip allowing access to daily activities.
Occupational therapists take part in selecting raw materials, designing splints, taking measurement, as well as manufacturing and controlling splints.